Polydopamine-mediated covalent functionalization of collagen on a titanium alloy to promote biocompatibility with soft tissues†
Abstract
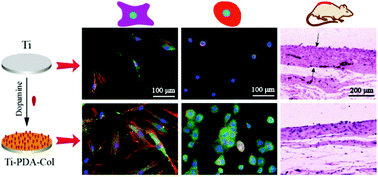
The clinical success of a titanium (Ti) percutaneous implant requires the integration with soft tissues to form a biological seal, which effectively combats marsupialization, premigration and infection after implantation. However, the bioinert surface of Ti or its alloys prevents the material from sufficient biological sealing and limits the application of Ti or its alloys as percutaneous implants. In this study, we achieved a collagen coating to bioactivate the surface of Ti-6Al-4V. In order to enable covalent functionalization, we first deposited a polydopamine (PDA) coating on Ti-6Al-4V based on dopamine self-polymerization and then immobilized collagen chains on PDA. Compared with physical absorption, such a chemical bonding method through mussel-inspired chemistry showed better stability of the coating. Meanwhile, the cellular tests in vitro indicated that collagen functionalization on the Ti-6Al-4V surface showed better adhesion of human foreskin fibroblasts (HFFs) and human immortal keratinocytes (HaCaTs). The subcutaneous implantation tests in rats indicated that the collagen modification attenuated soft tissue response and improved tissue compatibility compared with either pure Ti-6Al-4V or merely PDA coated samples. The facile bioinspired approach enables a persistent modification of metals by macromolecules under aqueous environments, and the PDA–collagen coated titanium alloy is worthy of further investigation as a percutaneous implant.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...