The nanoparticle-facilitated autophagy inhibition of cancer stem cells for improved chemotherapeutic effects on glioblastomas†
Abstract
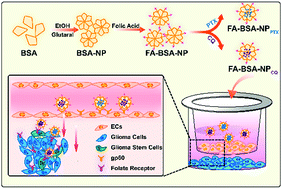
Due to the rapid growth of a tumor, the tumor cell metabolism becomes more active, resulting in the overexpression of albumin-binding proteins for transporting albumin as an energy and amino source. In that case, making use of nutrient transporters for targeted drug delivery to the brain becomes attractive. Herein, we synthesized albumin nanoparticles by a desolvation process, modified them with folic acid to enhance blood-brain-barrier (BBB) penetration and cellular uptake, and then loaded them with the antitumor drug paclitaxel (PTX) and autophagy inhibitor chloroquine (CQ) for combination therapy. The albumin nanoparticles could cross the BBB and target glioma cells effectively, and the combination therapy of PTX and CQ induced more cell apoptosis than PTX treatment alone in vitro. The results of the role of autophagy in the sensitivity of chemotherapeutic PTX to glioma cells showed that the stemness-associating genes (SOX2, POU5F1 and NANOG) of live glioma cells increased in the presence of PTX, while they dropped sharply with the combination including CQ. More importantly, it was found that the combined delivery system FA-BSA-NPPTX/CQ exhibited the most effective cell apoptosis. Our findings demonstrated that drug-loaded albumin nanoparticles could facilitate a combination of chemotherapy and autophagy inhibition for effective glioma therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...