Tuning of thermoresponsive pNIPAAm hydrogels for the topical retention of controlled release ocular therapeutics
Abstract
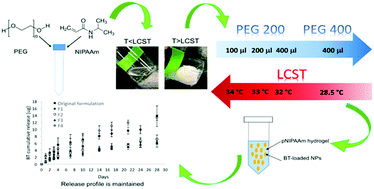
Low patient compliance and poor bioavailability of ophthalmic medications are the main limitations of topical eye drops. A potential solution to these disadvantages could be provided by thermoresponsive hydrogels, which could be used as the basis for a gelling eye drop for long-term release of therapeutics. We previously reported such a system capable of being retained in the lower fornix of rabbits, continuously releasing an anti-glaucoma drug for one month. Here, we sought to improve the properties of the existing gels as most relevant to patient use without altering the drug release profile. Specifically, we optimized the sol-to-gel transition temperature and de-swelling kinetics of pNIPAAm gels to avoid risk of the gelled drop reverting to liquid during cold or windy weather, and ensure quick gelation upon administration. A reduction of the gel LCST, faster gelation kinetics, and suitable viscosity for the administration as an eye drop were successfully achieved through modification of the poly(ethylene glycol) content in the water phase and its molecular weight. Our data suggest that drug release is not affected by these changes, with representative drug concentration profiles of the previous and new formulations demonstrating comparable anti-glaucoma release kinetics.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...