A novel fluorescent nanocellulosic hydrogel based on carbon dots for efficient adsorption and sensitive sensing in heavy metals
Abstract
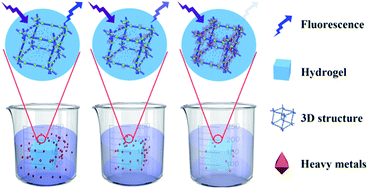
To take advantage of the high aspect ratio of cellulose nanofibrils (CNFs) and high performance luminescence of carbon dots (CDs), a novel fluorescent nanocellulosic hydrogel was synthesised and used not only as an effective adsorbent for the removal of heavy metals, but also as an optical sensor for the detection of heavy metals. This fluorescent nanocellulosic hydrogel was characterized with respect to its morphological features, chemical composition and optical properties by means of optical microscopy, SEM, XRD, FTIR, UV-vis and fluorescence spectroscopy. The effects of contact time and initial concentration on the adsorption performance of the nanocellulosic hydrogel were investigated. Based on the experimental results, the maximum adsorption capacities for Fe3+, Ba2+, Pb2+ and Cu2+ were 769, 212, 2056 and 1246 mg g−1, respectively. The prepared fluorescent nanocellulosic hydrogel demonstrated strong blue fluorescence with a fluorescence quantum yield of 23.6%, and displayed high sensitivity for the detection of Fe3+. In this hydrogel, the CNFs modified with CDs not only facilitated hydroxyl-induced aggregation of heavy metals as the adsorption-aggregator, but also allowed a rapid visual response to heavy metals as the optical sensor, which increased the adsorption capacity of heavy metals, and improved the stability of the fluorescence signal and the sensitivity for determining the concentration of heavy metals.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...