Single-step exfoliation of black phosphorus and deposition of phosphorene via bipolar electrochemistry for capacitive energy storage application†
Abstract
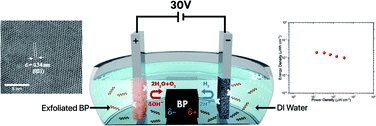
Black phosphorus (BP) is a two-dimensional material that has gained attention for various applications due to its exceptional physical and chemical properties such as tunable bandgap and high charge carrier mobility. However, the critical step towards the application of BP is still contingent on successfully exfoliating the bulk material into few-layer phosphorene nanosheets. Herein, we show a one-step, facile, and environmentally friendly method of bipolar electrochemical exfoliation-and-deposition of BP nanosheets on a positive feeding electrode. The exfoliated-and-deposited material is high-quality phosphorene with an orthorhombic crystal structure, and it adheres onto the substrate with a fractal and structured morphology. The electrochemical performance of the material was evaluated in a symmetric two-electrode configuration soaked in aqueous electrolyte for capacitive energy storage application. The results revealed fractional-order capacitive behaviour in the low-to-medium frequency, and a high stability and reversibility for at least 40 000 cycles. The power performance is outstanding with 0.35 mW cm−2 at a constant current rate of 0.5 mA cm−2.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...