A carbon microtube array with a multihole cross profile: releasing the stress and boosting long-cycling and high-rate potassium ion storage†
Abstract
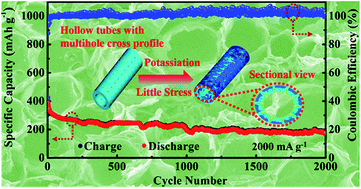
The abundance and low cost of potassium resources make potassium ion batteries (PIBs) a future energy storage system. However, it is difficult for current electrode materials to offer enough space to stably store large-sized potassium ions. In this study, using sycamore leaves as the raw material, a porous carbon microtube (PCM) array derived from carbon quantum dots (CQDs) is obtained. The resulting PCM features a multihole cross profile, high surface area (300.3 m2 g−1), and much larger interlayer spacing (0.396 nm). The experimental results and finite element analysis show that the PCM has a strong stable structure to release the stress against pulverization during cycling. As an anode material for PIBs, the PCM electrode displays a capacity of 177.6 mA h g−1 over 2000 cycles at a very high current density of 2000 mA g−1, which is among the best high-rate stabilities ever reported. In terms of cost effectiveness, long cycle lifespan and mass production, this work represents a brilliant prospect of anode materials for PIBs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...