Insights into the electrochemical processes of rechargeable magnesium–sulfur batteries with a new cathode design†
Abstract
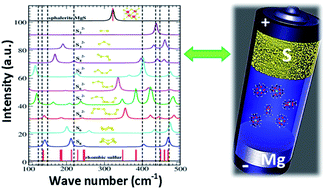
The present study shows the electrochemical performance of a room-temperature magnesium/sulfur (Mg/S) battery with a newly designed sulfur (3–0.5 mgsulfur cm−2) composite cathode. Operando Raman spectroscopy is employed to investigate the formation of polysulfide species at the cathode of Mg/S cells during the charge/discharge process, while density functional theory (DFT) calculations are used to correlate the Raman modes with a series of polysulfide species (Sxn−, x = 1–8). Operando Raman spectroscopy proves the chemical transformation from elemental sulfur (S8) via long and short chain polysulfides to magnesium sulfide upon discharge and conversion back to elemental sulfur during charging. Furthermore, the spectral measurements indicate the formation of a nanocrystalline magnesium sulfide with a cubic zinc blende phase at the end of discharge. The changes in the open circuit potential of the Mg/S cell during the resting period are investigated with the help of various spectroscopic techniques. These studies conclude that cell impedance is dominated by the anode side impedance due to the formation of a passivation layer under static conditions. Finally, the impedance studies under dynamic conditions verify that the applied electrode potential plays a significant role on the evolution of the anode interfacial impedance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...