Storage of Na in layered graphdiyne as high capacity anode materials for sodium ion batteries†
Abstract
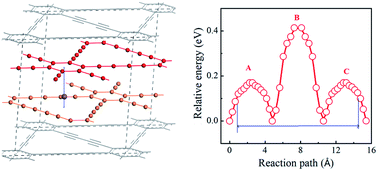
Layered carbon has been applied extensively in Li-ion batteries, and it may be expected to have potential application in Na-ion batteries (NIBs). However, graphite has a very low capacity of 35 mA h g−1 due to the weak interaction between Na ion and graphene layer. Layered graphdiyne with holes in each carbon layer is expected to enhance the binding between Na ion and carbon layer. Here we explore the storage of Na ions in layered graphdiyne for anodes of NIBs by first-principles methods with molecular dynamics simulations (MD). We find that there is suitable binding between Na and graphdiyne layers due to the carbon chain and that Na can intercalate into graphdiyne with a very high concentration of ∼0.8 (NaxC with x = 0.8) without the formation of Na clusters. The MD results indicate that the structure becomes thermally unstable when the concentration of Na loading was more than 0.78. From the insertion voltage, Na loading up to 0.61 is electrochemically favorable and thus the capacity goes up to 1237 mA h g−1. This is approximately 35 times higher than that of graphite. Layered graphdiyne is therefore likely to be an efficient and stable anode with high capacity suitable for high performance NIBs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...