Three-dimensional nitrogen and phosphorus co-doped carbon quantum dots/reduced graphene oxide composite aerogels with a hierarchical porous structure as superior electrode materials for supercapacitors†
Abstract
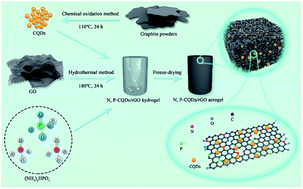
Carbon quantum dot (CQD)-based electrode materials as a novel kind of emerging materials have recently received increasing interest owing to their many unique properties. Herein, graphitic CQDs are synthesized by a modified chemical oxidation approach, and further utilized as the intercalator to prepare novel three-dimensional (3D) N, P co-doped CQDs/reduced graphene oxide (rGO) composite aerogels (N, P-CQDs/rGO) by a one-step hydrothermal approach. When used as an electrode material for supercapacitors for the first time, the as-obtained N, P-CQDs/rGO exhibits a notably enhanced specific capacitance (453.7 F g−1 at 1 A g−1) compared with GO, rGO, N, P-rGO and CQDs/rGO. Moreover, the as-synthesized N, P-CQDs/rGO presents excellent rate properties (69.5% of capacitance retention at 50 A g−1) and cycle performance (93.5% of capacity retention at 10 A g−1 over 10 000 cycles). The good capacitive behaviors can be ascribed to the synergistic effect of N, P co-doping modification, the introduction of CQDs and the unique 3D porous aerogel structure with a large specific surface area, hierarchical porous structure and superior electrical conductivity. In addition, a symmetrical device is assembled based on the N, P-CQDs/rGO composite aerogel, achieving a high energy density of 15.69 W h kg−1 at a power density of 325 W kg−1, and superior cycle stability with 85.5% of capacitance retention at 5 A g−1 over 10 000 cycles. This current work can offer a promising strategy for the design and development of novel and high-performance 3D CQD-based composite aerogels for application in supercapacitors and other energy storage systems.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...