Chemical fixation of carbon dioxide catalyzed via covalent triazine frameworks as metal free heterogeneous catalysts without a cocatalyst†
Abstract
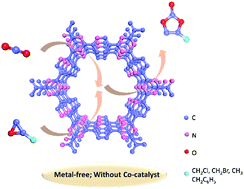
The synthesis of cyclic carbonates from the catalytic coupling of carbon dioxide (CO2) and epoxides is regarded as an efficient approach for the production of important industrial feedstock through the chemical fixation of CO2. However, most of the existing catalysts for this reaction are commonly existing on noble metal sites, and toxic co-catalysts and harsh reaction conditions are ineluctable. Herein, a set of new metal-free covalent triazine frameworks (2,5-DCP-CTF) was synthesized by the trimerization of 2,5-dicyanopyridine (2,5-DCP) exhibiting a hierarchical porous structure and high nitrogen content. In the absence of any co-catalyst and solvent, excellent catalytic activities for the conversion of CO2 to cyclic carbonates were achieved under mild conditions, and the best conversion rate and selectivity were 99.1% and 95.5%, respectively. This new CTF material can be a more environmentally friendly catalyst for the preparation of cyclic carbonates by the chemical fixation of carbon dioxide.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...