Dendrimers and hyper-branched polymers interacting with clays: fruitful associations for functional materials
Abstract
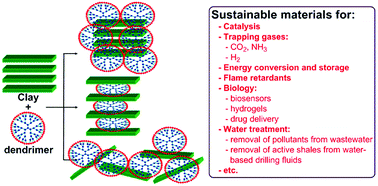
The possibility to incorporate diverse chemical species inside clays, especially swelling clay minerals, has been known for more than two millennia, but the first examples of man-made polymers interacting with clays only date back to about 30 years ago. Dendrimers and hyper-branched polymers differ from classical polymers by their intrinsically 3-dimensional structure, and by their large number of reactive functional groups. The study of their interaction with clays/clay minerals is relatively recent. Besides the fundamental research done on these kinds of organoclays, different potential uses have already been investigated. In this review, we will present an overview of the studies dealing with the synthetic processes, and the characterization of the resulting dendrimer/hyper-branched polymer–clay mineral (nano)composites. Special attention will be focussed on the properties of these new hybrid smart materials, in different fields ranging from catalysis, trapping gases (in particular CO2 and H2), energy conversion and storage, flame retardants, and biology (biosensors, hydrogels, and drug delivery) to water treatment (wastewater and water-based drilling fluids).
- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent Review Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...