Discovering a selective semimetal element to increase hematite photoanode charge separation efficiency†
Abstract
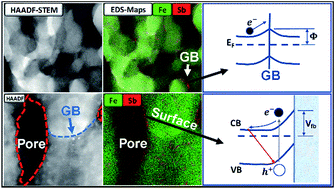
This work describes a colloidal deposition process that exploits the thermal spreading ability of Sb over a hematite surface to obtain a mesoporous film with extensive open porosity and high degree of Sb5+ dispersion. The addition of Sb increased the efficiency of water oxidation by a factor of 4.5 and photocurrent at 1.23 VRHE by a factor of 6.5 compared to those of an unmodified hematite film prepared under the same conditions. The overall efficiency increase for water oxidation is attributed to more efficient charge separation. Sb was found to be an excellent selective semimetal modifier with high dispersion over the material.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...