Cyclophosphazene-based hybrid polymer electrolytes obtained via epoxy–amine reaction for high-performance all-solid-state lithium-ion batteries†
Abstract
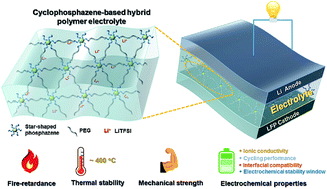
A polymer electrolyte (PE) is considered as a kind of promising candidate in lithium batteries due to its high energy density and no leakage issue compared to the liquid electrolyte. However, poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO)-based electrolytes also have some problems such as inferior mechanical strength, low ionic conductivity, poor thermal stability, and flammability. These flaws often trigger a short circuit due to the growth of lithium dendrites, restrict the potential applications of lithium-ion batteries, and cause severe safety problems. Herein, we proposed a strategy to overcome these defects. Hexa(4-aminophenoxy)cyclotriphosphazene (HAmCP) was utilized as the core, and polyethylene glycol diglycidyl ether (PEGDE) was employed as the cross-linking agent via a facile amino-epoxy reaction. The structure and purity of the substrate were confirmed by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and nuclear magnetic resonance (1H, 13C, and 31P NMR) characterizations. The formed network polymer electrolyte was mechanically robust and flexible owing to the hybrid cyclophosphazene core and the cross-linked structure. The PE was thermally stable under the temperature of 368 °C with 5% decomposition of the polymer matrix and could be stretched up to 127% elongation without break. Meanwhile, the PE also exhibited fire-retardant ability to some extent compared with the pure PEO-based polymer matrix formed via the radical polymerization of polyethylene glycol diacrylate (PEGDA). Furthermore, the all-solid-state PE possessed ionic conductivity up to 10−4 S cm−1 at 30 °C and excellent interfacial stability with a lithium anode, thus contributing to stable cycling for high-performance batteries.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...