Halogen-bond driven self-assembly of perfluorocarbon monolayers on silicon nitride†
Abstract
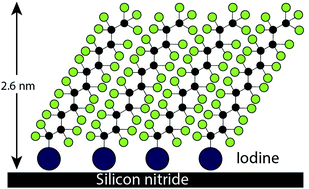
The self-assembly of a single layer of organic molecules on a substrate is a powerful strategy to modify surfaces and interfacial properties. Thiolates, silanes, phosphonates and carboxylates are widely used head-groups to link organic molecules to specific surfaces. In this study we show that self-assembly of perfluorododecyl iodide (I-PFC12) on a silicon nitride substrate leads to stable and highly compact monolayers of reproducible thickness (2.6 nm). Remarkably, the monolayers have the lowest ever reported surface energy of 2.6 mJ m−2. The most likely mechanism leading to the formation of the monolayers is halogen bonding between the iodine in I-PFC12 and the nitrogen and oxygen atoms on the nitride. As a convenient, flexible and simple method, the self-assembly of halogen-bond driven perfluorocarbon monolayers is compatible with several applications, ranging from biosensing to electronics and microfluidics. Compared to other methods used to functionalise surfaces and interfaces, our procedure offers the unique advantage to work with extremely inert perfluorinated solvents. We demonstrate that surfaces commonly unstable in contact with many common organic solvents, such as organic–inorganic perovskites, can be functionalized via halogen bonding.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...