Surface activation of cobalt oxide nanoparticles for photocatalytic carbon dioxide reduction to methane†
Abstract
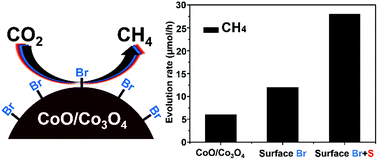
Cobalt oxide nanoparticles, by surface activation, successfully promoted photocatalytic CO2 reduction with a high efficiency and selectivity in aqueous media. Treatment with N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) resulted in the formation of an active form of Co3O4, removed surfactants, and coordinated Br on the surface, thereby enhancing the catalytic efficiency of CO2 reduction to methane.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...