Planar NiC3 as a reversible anode material with high storage capacity for lithium-ion and sodium-ion batteries†
Abstract
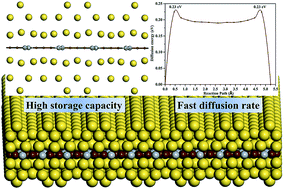
The recent discovery of a class of desirable anode materials in metallic two-dimensional (2D) transition-metal (TM) carbides has reignited great interest in the search for high-performance rechargeable lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) and sodium-ion batteries (SIBs). Using an unbiased structure search combined with first-principles calculations, here we identify an entirely planar NiC3 monolayer as a highly symmetric anode material that fully utilizes the active adsorption sites in the NiC4 unit and maintains the original active adsorption sites in the n-biphenyl unit. The outstanding stability of the NiC3 monolayer is confirmed by its superior cohesive energy, positive phonon modes, high thermal stability and strong mechanical stability. Intriguingly, the current design of entirely planar NiC3 monolayer demonstrates extraordinary ultrahigh storage capacity, fast charge/discharge capability and low open-circuit voltage. In particular, the capacity for Li and Na storage on the NiC3 monolayer reaches 1698 mA h g−1, ∼33% higher than the previously reported record (1278 mA h g−1 in puckered TiC3 monolayer) for 2D materials. The present results have broad implications for other 2D carbides as reversible anode materials for LIBs and SIBs that likely harbor similar novel functional performance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...