High Li+ transference gel interface between solid-oxide electrolyte and cathode for quasi-solid lithium-ion batteries†
Abstract
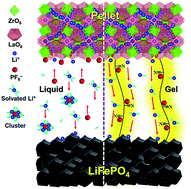
Solid-oxide electrolytes (SEs) are an alternative to using conventional organic liquid electrolytes for lithium ion batteries (LIBs) and offer solutions to the challenges associated with safety and energy density. However, SE-based LIBs suffer from high interfacial resistance between the electrolyte and electrodes. In this study, we develop a gelled poly(acrylonitrile-co-methyl acrylate) (P(AN-co-MA)) framework to facilitate Li+ transfer across the interface between an SE pellet of garnet-type Li6.75La3Zr1.75Ta0.25O12 (LLZTO) and a LiFePO4 cathode. The gelled polymeric framework exhibits high ionic conductivity and a large Li+ transference number (tLi+) of 0.67 that results from the synergy between the nitrile and acrylate functionalities and minimizes the formation of ion–solvent clusters and mobility of PF6− anions. The large tLi+ characteristic is advantageous for forming a junction with SEs featuring a unity tLi+ and suppressing polarization caused by PF6− accumulation. When coupled with the LLZTO pellet, the gel polymer electrolyte may exhibit collimated Li+ transport that suppresses Li-dendrite formation. The resulting Li|LLZTO|LiFePO4 battery demonstrates outstanding capacity (e.g., 154 mA h g−1 at 0.1 mA cm−2 and 25 °C), high rate retention, and excellent cycling stability. The present study demonstrates that the gelled P(AN-co-MA) framework acts an ideal interface between the SE and cathode for fabricating quasi-solid LIBs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...