Enhanced performance and stability of p–i–n perovskite solar cells by utilizing an AIE-active cathode interlayer†
Abstract
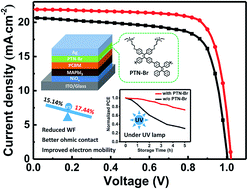
A new alcohol-soluble AIE-active quaternary ammonium salt PTN-Br was prepared and developed as the cathode interfacial layer (CIL) between the Ag electrode and [6,6]-phenyl-C61-butyric acid methyl ester (PCBM) in p–i–n perovskite solar cells (PVSCs). Excitingly, the device showed a reduced work function (WF) of the commonly used Ag electrode, improved cathode interfacial contact, accelerated electron transport mobility and suppressed interfacial recombination, directly leading to a champion power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 17.44%, which exceeded that of the reference device without PTN-Br as the CIL (15.14%). Also, thanks to the absorption of PTN-Br in the UV region, the PTN-Br-based PVSCs showed superior UV stability, maintaining 72.2% of the original PCE, to the control device which maintained only 36.8% of the initial PCE after UV irradiation for 12 h.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...