Core–shell MOF-derived N-doped yolk–shell carbon nanocages homogenously filled with ZnSe and CoSe2 nanodots as excellent anode materials for lithium- and sodium-ion batteries†
Abstract
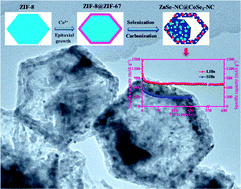
A novel and careful design of N-doped yolk–shell carbon nanocage homogenously filled with ZnSe and CoSe2 nanodots derived from core–shell ZIF-8@ZIF-67 was formulated for use as an anode in LIBs/SIBs. In this unique structure, ZnSe and CoSe2 nanodots were homogeneously distributed in the confined carbon network with hollow interiors. This kind of complexed structure can offer several attractive features, as follows. (a) The two transition metal selenides, namely, ZnSe and CoSe2, acting as active anodic materials can induce unique semiconducting characteristics and relatively high theoretical capacities. (b) The interfacial effect (built-in potential) between ZnSe and CoSe2 can effectively accelerate the diffusion rates of lithium/sodium ions in the solid. (c) The MOF-derived N-doped amorphous carbon with high mesoporosity—acting as a confined reactor—can increase the thermodynamic stability, inhibit structural instability, and alleviate unavoidable volume variations of the active materials. The hollow interior in a single carbon nanocage could provide a large void space, further buffering the volume change and stabilizing the structure during charge–discharge. Inspired by these merits, the as-obtained ZnSe-NC@CoSe2-NC, when used as an anode for LIBs and SIBs, can exhibit superior electrochemical performances with a reversible charge storage capacity of 717.8 mA g−1 after 600 cycles at a current density of 0.2 A g−1 in LIBs and 308.5 mA g−1 after 150 cycles at a current density of 0.1 A g−1 in SIBs. Even when tested in full-cell LIBs, the electrochemical results are promising. These electrochemical results were also confirmed by density functional theory calculations.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...