Heterogeneous single-site synergetic catalysis for spontaneous photocatalytic overall water splitting†
Abstract
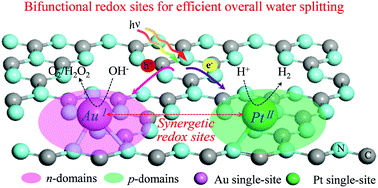
The development of photocatalysts with synergetic bifunctional catalytic centers is of great importance for efficient photocatalytic water splitting towards sustainable conversion and storage of renewable solar energy. Here, we present a conceptual design of atomic-level bifunctional redox single sites to realize an efficient catalytic reaction of photoexcited electron–hole pairs on g-C3N4-based photocatalysts for spontaneous overall water splitting. The atomically dispersed heterogeneous Pt1Nx–Au1Nx redox single sites anchored on a g-C3N4 support could successfully introduce p–n coupled micro-domains as effective bifunctional electron-donor–acceptor centers, which significantly improves the electron–hole separation efficiency to ∼60% in the visible-light region of 400–450 nm which is 6–10 times that of individual Pt/C3N4 and Au/C3N4. The bifunctional Pt–Au/C3N4 single-site photocatalyst could thus effectively split pure water with a reduced surface redox reaction barrier by ∼300 mV, resulting in ∼10-fold enhancement of the photocatalytic performance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...