Highly selective separation of H2S and CO2 using a H2S-imprinted polymers loaded on a polyoxometalate@Zr-based metal–organic framework with a core–shell structure at ambient temperature
Abstract
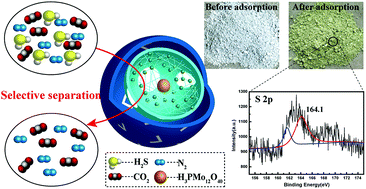
The removal of H2S is extremely important for industrial development owing to its corrosiveness, toxicity and unpleasant odor. In industrial gas streams, however, the existence of CO2 affects the removal efficiency of H2S. To improve the removal of H2S and recovery of sulphur resources at ambient temperature, we designed novel core–shell-structured H2S imprinted polymers (PMo12@UiO-66@H2S-MIPs) based on the surface of UiO-66 modified by phosphomolybdic acid hydrate. Using H2O as a substitution template for H2S avoids the toxicity and instability issues of H2S. The polymerization conditions, including the mole ratio of templates/functional monomers/cross-linkers, the amount of porogens, and the polymerization time, were optimized in detail. PMo12@UiO-66@H2S-MIPs exhibited high adsorption capacity for H2S at ambient temperature even in the presence of water steam and showed excellent separation for H2S/CO2. Air purge regenerated PMo12@UiO-66@H2S-MIPs at 180 °C and O3 treatment at room temperature can maintain their stable desulfurization ability for at least 6 cycles. The H2S was transformed into sulphur after adsorption, and PMo12 played the redox role in the desulfurization process. This work broadens the horizon for H2S removal, separation and resource utilization.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...