Mass production of graphene materials from solid carbon sources using a molecular cracking and welding method†
Abstract
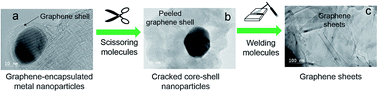
A novel process is developed for high-volume production of low-cost graphene materials from any solid carbon resources, especially biomass sources. Few-layer graphene materials from solid carbon resources are produced through a molecular cracking and welding (MCW) method. The MCW technique is a single step process with two stages, i.e., graphene-encapsulated core–shell nanoparticles are first formed by catalytic thermal treatment of solid carbon materials. Then in the second stage these core–shell structures are opened by ‘cracking molecules’, and the cracked graphene shells are self-welded and reconstructed to form high quality multilayer graphene materials at a heating temperature with selected welding reagent gases. This novel graphene material with super hydrophobic properties can be used to filter water from crude oil emulsions in the petroleum industry.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...