Synergistic effects of temperature and polarization on Cr poisoning of La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3−δ solid oxide fuel cell cathodes†
Abstract
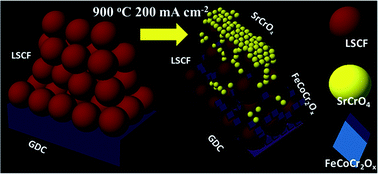
La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3−δ (LSCF) solid oxide fuel cell cathodes were poisoned by Cr at different temperatures and polarization conditions with a Cr–Fe alloy as the interconnect. Cr induced degradation was analysed by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) focusing on the electrochemical resistance (Rchem) that reflects the cathode electrochemical properties. It was found that Rchem increased more with increasing temperatures. However cathodic polarization exhibited a synergistic effect with the temperature, which accelerated the LSCF cathode degradation at 800 °C while lowering the degree of degradation at 900 °C. By correlating complementary micro- and nano-scale microstructure characterization with the impedance analysis, the degradation mechanisms were investigated. A new Cr incorporation mechanism involving preferential formation of nanometre size Fe–Co–Cr–O spinel particles within the cathode up to the cathode/electrolyte interface was found to be responsible for the reduced degradation at 900 °C combined with cathodic polarization. The new mechanism reveals that the activity of B site elements in LSCF and possibly other perovskite cathodes plays an important role under certain combined temperature and polarization conditions, therefore future research in designing Cr resistant perovskite cathode materials may consider strategies that utilize the exsolution of B site elements for the formation of beneficial spinel phases.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...