Triggering highly stable catalytic activity of metallic titanium for hydrogen storage in NaAlH4 by preparing ultrafine nanoparticles†
Abstract
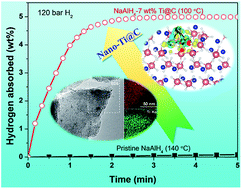
Highly stable catalytic activity of metallic Ti and corresponding mechanistic understanding are of particularly critical importance for the development of sodium alanate (NaAlH4) as an advanced on-board hydrogen storage medium. However, only limited catalytic effectiveness is observed for commercial metallic Ti powders due to their ductile behavior limiting the dispersion of large particles. Here, we successfully synthesize ultrafine metallic Ti nanoparticles (3–5 nm) supported on amorphous carbon (nano-Ti@C) through a facile, scalable calcination process. Unlike commercial metallic Ti powders, the nano-Ti@C exhibits remarkable catalytic activity for hydrogen storage in NaAlH4, superior to other reported transition metals and rare earth metals. The 7 wt% nano-Ti@C-containing NaAlH4 sample delivers a quite low onset temperature of dehydrogenation of 75 °C and a practically available hydrogen capacity as high as 5.04 wt%. Reloading of hydrogen is fully completed in <3 min at 100 °C and 120 bar H2; this sorption kinetics is fastest among all catalytically enhanced NaAlH4 systems known. Moreover, only 0.07 wt% of hydrogen capacity is lost after 100 cycles, exhibiting a highly stable cyclability. Theoretical calculations reveal the interaction between Ti and Al, which not only weakens the Al–H bonding but also facilitates diffusion of H in NaAlH4, contributing to the superior catalytic activity of nano-Ti@C. Our findings greatly increase potentials towards practical applications of catalyst-doped NaAlH4 for onboard hydrogen storage.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2019 Journal of Materials Chemistry A HOT Papers


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...