Li/Fe substitution in Li-rich Ni, Co, Mn oxides for enhanced electrochemical performance as cathode materials†
Abstract
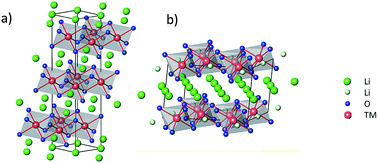
Li-rich nickel cobalt manganese (NCM) oxides are among the most promising cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries owing to their high specific charges and operating voltages. However, their crystal structures are unstable upon prolonged cycling, leading to a collapse of their electrochemical performance. In this study, we investigated Fe doping of Li-rich NCM materials and explored various Li/Fe ratios. Compared with the reference Li-rich NCM material, the Li1.16(Ni0.18Co0.10Mn0.52Fe0.02)O2 composition exhibited a higher specific charge, potential drop mitigation at fast cycling rates, and an enhanced rate capability. At a rate of 4C, this composition exhibited a specific charge of 150 mA h g−1, which was as much as 50% higher than that of the reference (100 mA h g−1). Neutron and X-ray diffraction data for compounds with different Fe doping concentrations indicated that the crystallographic structure was preserved with up to 2 mol% Fe without the formation of separate impurity phases. Furthermore, we found that the crystal structure of this Fe-doped material was less susceptible to the effects of prolonged cycling than the reference compound. Complementary investigations with X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy revealed that Fe was electrochemically active in the structure, which explains the beneficial effects observed with Fe doping of Li-rich NCM materials, such as an increased specific charge and more stable cycling.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...