Fast and scalable wet-spinning of highly conductive PEDOT:PSS fibers enables versatile applications†
Abstract
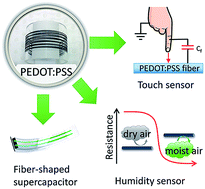
Highly conductive, strong and flexible fibers are important for the realization of many high technological applications including smart textiles, flexible electrodes, and fast-response sensors and actuators. Here, we report a facile one-step method to produce highly conducting poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):poly(4-styrenesulfonate) (PEDOT:PSS) fibers that effectively removes the insulating PSS component within seconds, thereby enabling their fabrication in a fast one-step process. The highest electrical conductivity for a ∼15 micron fiber (3828 S cm−1) is comparable to that for very thin PEDOT:PSS film produced to date (4380 S cm−1 for 100 nm film). These fibers can withstand mechanical mistreatment – testing has been conducted in various environments including sonication and exposure to boiling water for extended periods. The study on the mechanism of conductivity enhancement shows that our spinning method efficiently removes the PSS component during fiber formation and improves orientation of the PEDOT chains, which facilitates efficient intramolecular and intermolecular charge transport, leading to the enhancement in electrical properties. We demonstrate that these highly conducting fibers can be used for fast response and highly sensitive touch sensors, body moisture monitoring, and long fiber-shaped supercapacitors. These results provide a scalable platform for the fabrication of highly conductive fibers with excellent mechanical properties, which are essential characteristics required for many advanced applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...