Engineering Fe-doped highly oxygenated solvothermal carbon from glucose-based eutectic system as active microcleaner and efficient carbocatalyst†
Abstract
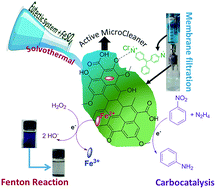
Solvothermal carbon (STC) has emerged as an exciting functional material for diverse applications. However, designing STCs with tunable properties (for instance shape, chemical functionalities, and surface acidity) for on-demand applications is challenging. Herein, a novel strategy was developed to engineer advanced STCs with different architectures using a glucose-based eutectic system and FeSO4 under solvothermal conditions. The resulting materials were characterized using different analytical tools, which confirmed the formation of STCs with a defined shape (sheets or spheres depending on the reaction conditions), high surface area (26–175 m2 g−1), and highly oxygenated (O/C ratio = 0.41–0.55) functionalities. The nanoscale H-bonding network present in the eutectic system plays a role in the formation of enhanced oxygen functionalities; whereas, the existence of Fe-salt facilitates the construction of a sheet-like morphology with improved surface acidity. Taking advantage of their remarkably high carboxyl content (62.6–87.8 mmol g−1) and Fe-doping (0.11–0.56%), the STCs were successfully employed as microcleaners for the selective removal of cationic pollutants (organic dyes and drugs) and as a catalyst for dye degradation. Under the optimized conditions, the obtained STC showed >95% removal efficiency for cationic pollutants with 90% selectivity (compared to anionic pollutants), high flux and rejection (flux = 603 L m−2 h−1 and rejection = 96%) and superior adsorptive capacity (qm = 689.7 mg g−1, which is 3–16 fold higher than that reported for hydrothermal carbon). Both the adsorbed dye and drug were successfully desorbed from the STCs and degraded completely by Fenton catalysis, while the adsorbent maintained >90% removal efficiency during five cycles; thus, demonstrating their utility as active microcleaners. Further, the resulting STCs showed potential as carbocatalysts for the facile reduction of nitrobenzene to aniline with 95% conversion efficiency and 63% yield, and therefore, can also be envisaged as effective carbocatalysts for sustainable catalysis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...