Vertically aligned carbon fibers as supporting scaffolds for phase change composites with anisotropic thermal conductivity and good shape stability
Abstract
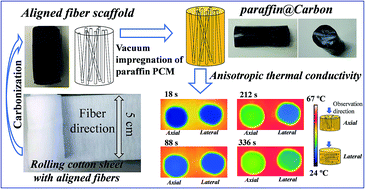
The wide application of organic phase change materials for thermal energy storage and management is limited by their low thermal conductivity and poor shape stability. In this work, anisotropic thermally conductive and shape-stabilized phase change composites (PCCs) were successfully prepared with vertically aligned carbon fibers as supporting scaffolds. The aligned and hollow carbon fiber scaffolds with different densities were facilely fabricated by the direct carbonization of rolled cotton sheets with aligned and hollow cellulose fibers. PCCs were obtained by vacuum impregnation of paraffin wax. Because of the interconnected hollow carbon fiber frameworks with vertically aligned fibers and high porosity, PCCs present enhanced anisotropic thermal conductivity and good shape stability against leakage. The thermal conductivity in the axial direction along the fibers is higher than that in the lateral direction, since the aligned fiber scaffolds act as the thermal conduction pathway. The thermal conductivity of a PCC with a carbon ratio of 8.8 wt% is 0.77 W K−1 m−1 (>3 times that of pure paraffin) in the axial direction, while the value in the lateral direction is 0.58 W K−1 m−1. This work provides a novel strategy for designing anisotropic thermally conductive and shape-stabilized PCCs with potential applications in advanced thermal management and storage.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...