Simulation of H2/CH4 mixture permeation through MOF membranes using non-equilibrium molecular dynamics†
Abstract
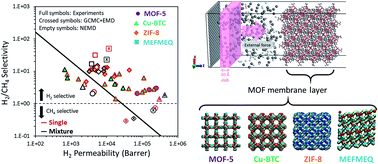
Grand canonical Monte Carlo (GCMC) simulations are widely used with equilibrium molecular dynamics (EMD) to predict gas adsorption and diffusion in single-crystals of metal–organic frameworks (MOFs). Adsorption and diffusion data obtained from these simulations are then combined to predict gas permeabilities and selectivities of MOF membranes. This GCMC + EMD approach is highly useful to screen a large number of MOFs for a target membrane-based gas separation process. External field non-equilibrium molecular dynamics (NEMD) simulations, on the other hand, can directly compute gas permeation by providing an accurate representation of MOF membranes but they are computationally demanding and require long simulation times. In this work, we performed NEMD simulations to investigate H2/CH4 separation performances of MOF membranes. Both single-component and binary mixture permeabilities of H2 and CH4 were computed using the NEMD approach and results were compared with the predictions of the GCMC + EMD approach and experimental measurements reported in the literature. Our results showed that there is a good agreement between NEMD simulations and experiments for the permeability and selectivity of MOF membranes. NEMD simulations provided the direct observation of the mass transfer resistances on the pore mouth of MOF membranes, which is neglected in the GCMC + EMD approach. Our results suggested that once the very large numbers of MOF materials were screened using the GCMC + EMD approach, more detailed NEMD calculations can be performed for the best membrane candidates to unlock the actual gas transport mechanism before the experimental fabrication of MOF membranes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...