Influence of the ion size on the stability of the smectic phase of ionic liquid crystals†
Abstract
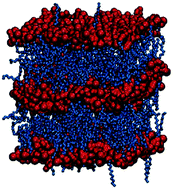
The thermotropic phase behavior of ionic liquids and ionic liquid crystals based on novel N-alkyl-3-methylpyridinium halides, trihalides and dichloroiodates was experimentally studied by polarized optical spectroscopy (POM) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) as well as by molecular dynamics (MD) simulation. In the experiments, the existence and thermal range of stability of the smectic phase of these ionic liquid crystals are found to strongly depend on the volume ratio between the cation and anion, that is their relative size. Only compounds with a relatively large volume ratio of the cation to anion, i.e., those with longer cationic alkyl chains and monoatomic halide anions, have a stable smectic A phase. Both melting points and clearing points increase with such a ratio. The MD simulation results qualitatively agree very well with the experimental data and provide molecular details which can explain the experimentally observed phenomena: the stronger van der Waals interactions from the longer alkyl chains and the stronger electrostatic interactions from the smaller anions with a higher charge density increase the stability of both the crystal phase and the smectic phase; this also prevents the ionic layers from easily mixing with the hydrophobic regions, a mechanism that ultimately leads to a nanosegregated isotropic liquid phase.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...