Bio-based thermoplastic poly(butylene succinate-co-propylene succinate) copolyesters: effect of glycerol on thermal and mechanical properties†
Abstract
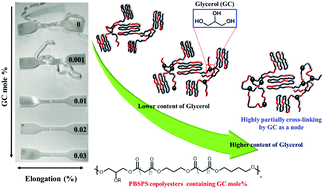
Poly(butylene succinate-co-propylene succinate) (PBSPS) was polymerized using succinic acid, 1,4-butanediol, 1,3-propanediol, and glycerol (GC). The PBSPS copolyester with a BS/PS ratio of 7/3 has a low melting point (Tm, 80 °C) and crystallization temperature (Tc, 20 °C) in addition to excellent thermal stability with a thermal degradation temperature (Td) above 300 °C. Isodimorphism was observed for 30–50 mol% PS, lowering Tm and Tc. The featured crystalline lattices (021) and (110) of PBS at 2θ = 21.5° and 22.5° gradually disappeared with PS content greater than 50 mol% and transformed into a PPS crystalline lattice at 2θ = 22.3°. Young's modulus decreased with increasing PS content due to crystallinity loss. Wide-angle X-ray diffraction demonstrated that the chain movement regularity was affected by the GC content, reducing the crystallinity. The PBSPS copolyesters were elastic with 0.001 mol% GC but became rigid with GC content greater than 0.01 mol%. The chain conformation was flexible for 0.001–0.01 mol% GC and exhibited an irregular steric architecture for 0.02–0.03 mol% GC due to more GC acting as nodes. Thus, the thermal and mechanical properties of the synthesized bio-based PBSPS copolyesters can be controlled by adjusting the GC content; therefore, such copolyesters are suitable for medical support, coating, and phase-change material applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...