A nature-inspired lubricant-infused surface for sustainable drag reduction†
Abstract
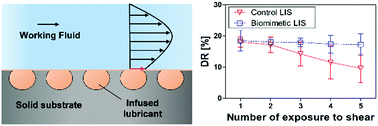
Reduction of frictional drag exerted on submerged marine vehicles results in considerable economic and environmental benefits. A lubricant-infused surface (LIS) inspired by Nepenthes pitcher was introduced as an emerging surface technology for substantial frictional drag reduction. However, the LIS easily loses its drag-reduction ability because the lubricant is easily depleted by shear stresses of external flow. In this study, a new biomimetic LIS with a unique surface topography is proposed to increase the sustainability of the infused lubricant. This biomimetic LIS has re-entrant shaped cavities in the surface, inspired by the mucus secretion and storage systems of loach, hagfish, and seaweed, whose skin can sustain slippery mucus layers even under continuous exposure to harsh seawater flow conditions. The slippery characteristics and enhanced sustainability of the biomimetic LIS were investigated by directly measurement of the slip length and pressure loss in channel flow over the LIS. The frictional drag reduction efficiency of the biomimetic LIS was measured to be approximately 18% compared with the corresponding no-slip surface. Moreover, the excellent sustainability of the biomimetic LIS was demonstrated by comparing the drag-reduction abilities before and after exposure to a high shear flow. The high durability might be attributed to the re-entrant shaped surface topography of the biomimetic LIS. The present results would provide insights into the design of a robust and sustainable LIS for practical drag reduction applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...