Tunable fabrication of concave microlens arrays by initiative cooling-based water droplet condensation†
Abstract
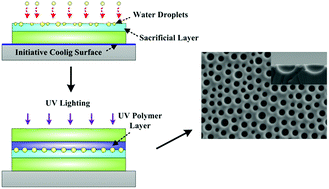
Microlens arrays (MLAs), as one of the key features in the optoelectronics field, have attracted a lot of attention recently. Unfortunately, existing fabrication methods of MLAs have many disadvantages, such as complex fabrication procedures and difficult morphology control. This paper presents a low-cost and tunable fabrication approach for concave MLAs on ultraviolet (UV) polymer surfaces. We used condensed water droplets, formed by initiative cooling, as the template for the formation of concave MLAs in this approach. A sacrificial layer of polymer material was introduced to fabricate concave MLAs with different morphology parameters. The three most important parameters of MLAs, i.e. diameter, cross-sectional profile, and packing distance, can be tuned by the proposed novel fabrication approach. By controlling the condensation time of water droplets, we can control the diameter of the concave MLAs. Moreover, the cross-sectional profile can be controlled by replacing the sacrificial layer material to change the interaction among the water droplets, sacrificial polymers, and UV polymers. In addition, the packing distance of the MLAs can also be adjusted by introducing the lateral flow of the sacrificial polymer, which was driven by the additional sacrificial polymer dispensed on the substrate. Furthermore, the UV polymer film with MLAs on its surface was applied for the packaging of high power green LEDs. Consequently, the optical output power of green LED modules is enhanced by 11.4% when using the MLAs at the driving current of 500 mA.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...