DNA functionalization of colloidal particles via physisorption of azide-functionalized diblock copolymers†
Abstract
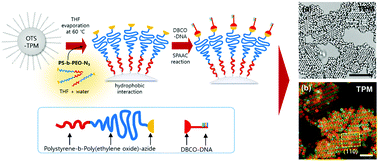
DNA-coated inorganic particles can be prepared simply by physical adsorption of azide-functionalized diblock copolymers (polystyrene-b-poly(ethylene oxide)-azide, PS-b-PEO-N3) onto hydrophobically-modified inorganic particles, followed by strain-promoted azide–alkyne cycloaddition (SPAAC, copper-free click chemistry). This approach is applied to organosilica, silica and titania particles. The DNA-coated colloids are successfully crystallized into colloidal superstructures by a thermal annealing process using DNA-mediated assembly.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...