Entry modes of ellipsoidal nanoparticles on a membrane during clathrin-mediated endocytosis
Abstract
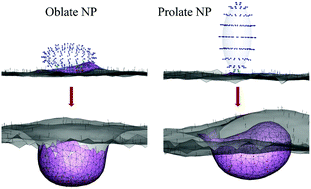
The membrane wrapping and internalization of nanoparticles, such as viruses and drug nanocarriers, through clathrin-mediated endocytosis (CME) are vitally important for intracellular transport. During CME, the shape of the particle plays crucial roles in the determination of particle–membrane interactions, but much of the previous work has been focused on spherical particles. In this work, we develop a stochastic model to study the CME of ellipsoidal particles. In our model, the deformation of the membrane and wrapping of the nanoparticles are driven by the accumulation of clathrin lattices, which is stimulated by the ligand–receptor interactions. Using our model, we systematically investigate the effect of particle shape (ellipsoids with different aspect ratios) on the CME. Our results show three entry modes: tip-first, tilted, and laying-down modes, used by ellipsoidal nanoparticles for internalization depending on the aspect ratio. Certain ellipsoids are able to take multiple entry modes for internalization. Interestingly, the prolate ellipsoid with an aspect ratio of 0.42 can be internalized with a significantly reduced number of ligand–receptor bonds. Particles which can be internalized with fewer bonds are excellent candidates for transcellular drug delivery. Moreover, our results demonstrate that internalization of ellipsoids with intermediate aspect ratios is easier than that of particles with low and high aspect ratios. Our model and simulations provide critical mechanistic insights into CME of ellipsoidal particles, and represent a viable platform for optimal design of nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...