Influence of surface topography attributes on settlement and adhesion of natural and synthetic species
Abstract
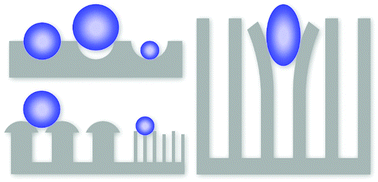
Surface topographies of various sizes, shapes, and spatial organization abound in nature. They endow properties such as super-hydrophobicity, reversible adhesion, anti-fouling, self-cleaning, anti-glare, and anti-bacterial, just to mention a few. Researchers have long attempted to replicate these structures to create artificial surfaces with the functionalities found in nature. In this review, we decompose the attributes of surface topographies into their constituents, namely feature dimensions, geometry, and stiffness, and examine how they contribute (individually or collectively) to settlement and adhesion of natural organisms and synthetic particles on the surface. The size of features that comprise the topography affects the contact area between the particle and surface as well as its adhesion and contributes to the observed adsorptive properties of the surface. The geometry of surface perturbations can also affect the contact area and gives rise to anisotropic particle settlement. Surface topography also affects the local stiffness of the surface and governs the adhesion strength on the surface. Overall, systematically studying attributes of surface topography and elucidating how each of them affects adhesion and settlement of particles will facilitate the design of topographically-corrugated surfaces with desired adsorption characteristics.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Soft Matter 15th Anniversary Perspectives


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...