Behavior of active filaments near solid-boundary under linear shear flow
Abstract
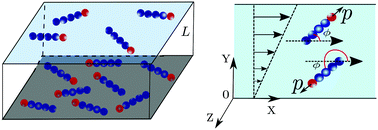
The steady-state behavior of a dilute suspension of self-propelled filaments confined between planar walls subjected to Couette-flow is reported herein. The effect of hydrodynamics has been taken into account using a mesoscale simulation approach. We present a detailed analysis of positional and angular probability distributions of filaments with varying propulsive force and shear-flow. The distribution of the centre-of-mass of the filament shows adsorption near the surfaces, which diminishes with the flow. The excess density of filaments decreases with Weissenberg number as Wi−β with an exponent β ≈ 0.8, in the intermediate shear range (1 < Wi < 30). The angular orientational moment also decreases near the wall as Wi−δ with δ ≈ 1/5; the variation in orientational moment near the wall is relatively slower than the bulk. It shows a strong dependence on the propulsive force near the wall, with variation on force as Pe−1/3 for large Pe ≥ 1. The active filament shows orientational preference with flow near the surfaces, which splits into upstream and downstream swimming. The population splitting from a unimodal (propulsive force dominated regime) to bimodal phase (shear dominated regime) is identified in the parameter space of propulsive force and shear flow.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...