Controlled release from PCL–alginate microspheres via secondary encapsulation using GelMA/HAMA hydrogel scaffolds†
Abstract
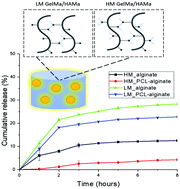
Controlling the release of bioactive agents has important potential applications in tissue engineering. While microspheres have been investigated to manipulate release rates, the majority of these investigations have been based on delivery into aqueous media, whereas the cellular environment in tissue engineering is more typically a hydrogel scaffold. If drug-loaded microspheres are introduced within scaffolds to deliver biologically active substances in situ, it is crucial to understand how the release rate is influenced by interactions between the microspheres and the scaffold. Here, we report the fabrication and characterization of a biodegradable scaffold that contains composite microspheres and is suitable for biological applications. Our approach evaluates the influence on the release profile of a model drug (FITC-dextran sulfate) from alginate and PCL–alginate microspheres within a hydrogel construct forming a secondary encapsulation. Increasing the degree of crosslinking in the secondary encapsulation matrix led to a slower cumulative release from 36% to 15%, from the alginate microspheres, whereas a decrease from 26% to 6% was observed for the PCL–alginate microspheres. These results suggest that the release of bioactive molecules can be fine tuned by independently engineering the properties of the scaffold and microspheres.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...