Diffusiophoresis in ionic surfactants: effect of micelle formation
Abstract
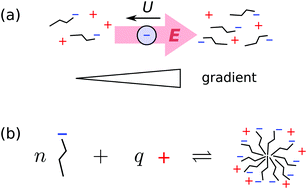
We explore the consequences of micelle formation for diffusiophoresis of charged colloidal particles in ionic surfactant concentration gradients, using a quasi-chemical association model for surfactant self assembly. The electrophoretic contribution to diffusiophoresis is determined by re-arranging the Nernst–Planck equations, and the chemiphoretic contribution is estimated by making plausible approximations for the density profiles in the electrical double layer surrounding the particle. For sub-micellar solutions we find that a particle will typically be propelled down the concentration gradient, although electrophoresis and chemiphoresis are finely balanced and the effect is sensitive to the detailed parameter choices and simplifying assumptions in the model. Above the critical micelle concentration (CMC), diffusiophoresis becomes much weaker and may even reverse sign, due to the fact that added surfactant goes into building micelles and not augmenting the monomer or counterion concentrations. We present detailed calculations for sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), finding that the typical drift speed for a colloidal particle in a ∼100 μm length scale SDS gradient is ∼1 μm s−1 below the CMC, falling to ≲0.2 μm s−1 above the CMC. These predictions are broadly in agreement with recent experimental work.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...