Surface passivation via acid vapor etching enables efficient and stable solution-processed CdTe nanocrystal solar cells†
Abstract
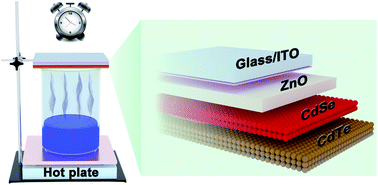
Achieving stable and low-resistance interfaces for hole transport layers with well-matched energy levels is crucial to maximize the performance of solution-processed CdTe nanocrystal (NC) based solar cells. Wet chemical etching with substrates immersed in dilute acid solutions is commonly adopted to modify traditional thick vacuum-evaporated CdTe layers for forming a conductive layer with good ohmic contact with the metal electrode. However, for next-generation low-cost solution-processed CdTe NC based solar cells, this method has failed so far since the acid (Br2/CH3OH or HNO3/H3PO4) can permeate easily into the grain boundaries of CdTe NCs and form a device shunt. Herein, a new technology called acid vapor etching (AVE) is developed for the first time for solution-processed CdTe NC solar cells. It's found that surface passivation can be well controlled during a mild bromine–methanol (BM) vapor etching process. Besides BM, other acid solutions such as a nitric–acetic (NA) acid solution are also suitable to adjust the CdTe interface, illustrating the remarkable universality of this method. The AVE-processed devices with an inverted configuration of ITO/ZnO/CdSe/CdTe/Au show very high efficiencies of 8.38% (BM) and 8.67% (NA) due to significant enhancement in short-circuit current, which are increased by ∼30% over that of a conventional device (5.83%) without AVE. Moreover, the AVE-processed CdTe NC solar cells show a striking improvement in stability, indicating their potential application in the manufacture of large-area solution-processed CdTe solar cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...