Surface structure-dependent electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 to C1 products on SnO2 catalysts†
Abstract
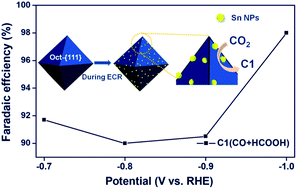
An alternative way to mitigate the energy and environmental crisis is electrochemical CO2 reduction (ECR) into high-value products using renewable energy. Recently, Sn-based catalysts have attracted attention because of their high ECR selectivity to C1 products (HCOOH and CO). However, high overpotential, low current density, and poor stability are some issues that need to be addressed for these Sn based ECR catalysts. Resolving these problems largely depends on a comprehensive insight into the relationship between the structure and the performance of the catalysts in the ECR. In this work, we specifically compared the ECR activities and selectivities of three kinds of SnO2 nanocrystals (NCs) with different dominantly exposed facets ({111}, {221} and {110}) in an effort to elucidate their surface structure–performance relationship. We found that {111} faceted octahedral SnO2 NCs (i.e., Oct-{111} NPs) showed not only high selectivity for C1 products (>90% FE) in a wide potential range of −0.7 V to −1.0 V but also significant stability. The performance of Oct-{111} NPs was superior to that of the other two SnO2 morphologies, i.e. {221} faceted SnO2 octahedral NCs and {110}-dominantly faceted SnO2 rod-like NCs. Detailed structure and composition analysis revealed that such different ECR performances of the three SnO2 facets were mainly related to the formation of different catalytic layers on their surfaces. The findings presented here will deepen our understanding of the surface-dependent performances of Sn-based electrocatalysts in the ECR. This work provides a new strategy to construct high performance electrocatalysts through rational regulation of the metal/oxide interface.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...