Trace molybdenum doped Li2RuO3 as a cathode material with enhanced performance for lithium ion batteries†
Abstract
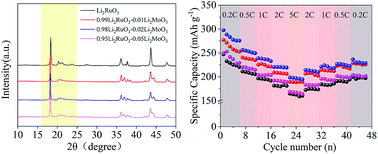
The widespread applications of lithium ion batteries in the energy storage field propel correlational research forward. To satisfy the increasing demand for high endurance and energy density of battery systems, various materials are proposed to study their electrochemical behaviour. The lithium-rich layered materials, as one of the high energy density cathode materials, exhibit a high specific capacity of ∼250 mA h g−1. However, during the cycling process, these materials may face problems like voltage fading, capacity loss, limited cycle life and so on. All of these drawbacks restrict their applications seriously. In recent years, many researchers have proposed various strategies including ionic doping and surface modification to ameliorate the structure and properties. In the present paper, we dope tetravalent molybdenum into Li2RuO3 to form a series of Li2RuO3–Li2MoO3 compounds. The doping products exhibit enhanced electrochemical lithium storage reversibility compared to the pristine Li2RuO3. In particular for 0.98Li2RuO3–0.02Li2MoO3, it possesses the best discharge performance on the basis of specific capacity (∼307 mA h g−1) at 0.2C and superior cycling performance. Based on the whole analysis, it can be concluded that trace Mo doping can implement an intensive improvement in electrochemical performance that originates mainly from the reversible anionic redox chemistry and charge transfer kinetics. Here, the observed results provide perspectives for future research on developing high performance cathode materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...