Hydrogen production by photocatalytic water splitting of aqueous hydrogen iodide over Pt/alkali metal tantalates†
Abstract
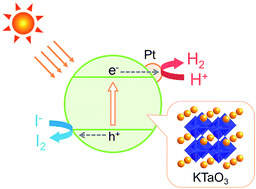
Photocatalytic hydrogen production from aqueous hydrogen iodide (HI) over alkali metal tantalates loaded with Pt (Pt/ATaO3, A = Li, Na, or K) was demonstrated. Of the photocatalysts examined, Pt/KTaO3 showed the highest photocatalytic activity for HI decomposition. KTaO3, having the lowest excitation energy, absorbs the largest number of photons for use in photocatalytic reactions, and its corresponding catalyst has the highest number of reaction sites owing to the excellent dispersion of the Pt cocatalyst. These results demonstrate the possibility of developing a new solar-energy-based water splitting process that can convert both light and thermal energy in sunlight to hydrogen energy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...