Nanosized titanium niobium oxide/carbon electrodes for lithium-ion energy storage applications†
Abstract
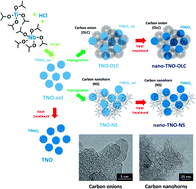
High demand for safer and more stable lithium-ion batteries brings up the challenge for finding better electrode materials. In this work, we study the functionalities of titanium niobium oxide (TNO)/carbon hybrid materials using carbon onions (OLC) and carbon nanohorns (NS), which are synthesized by well-controlled sol–gel chemistry, for anodes in lithium-ion batteries. We used two different molar ratios of titanium to niobium (1 : 2 and 1 : 5), and we compared the TNO–OLC and TNO–NS hybrid materials to conventional composite electrodes using physically admixed carbon. TNO–OLC-1:2 and TNO–OLC-1:5 nanohybrid materials displayed good electrochemical performance, with initial capacity values of 284 mA h g−1 and 290 mA h g−1, respectively, normalized to the metal oxide mass. Moreover, they maintained 68% (TNO–OLC-1:2) and 69% (TNO–OLC-1:5) of the initial capacity at 1 A g−1, outperforming the carbon nanohorn hybridized and composited electrode which maintained less than 50%. The long-term cycling stability of 800 cycles presents good capacity retention of 73% (TNO–OLC-1:2) and 76% (TNO–OLC-1:5), while the TNO–NS-1:2 hybrid material yields better capacity retention of 90% despite its low capacity. Our study demonstrates that the combination of TNO with appropriate carbon substrates enables good electrochemical performance but requires careful evaluation of the interplay of crystal structure, phase content, and particle morphology.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...