Biomimetic mitochondrial nanostructures boost the battery performance†
Abstract
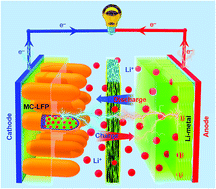
Mitochondrion is a dual membrane-bound biological nanostructure, which serves as a cellular power house in living organisms. Thus, its artificial counterparts have attracted high interest for application in batteries owing to their electrochemical energy transformation and storage functionalities. Inspired by the structural-functionality characteristics of the mitochondrion, herein, we report a biomimetic “mitochondrion lithium iron phosphate (MC-LFP)” for the first time to augment the performance of lithium-ion batteries. We adopted a two-step synthetic sequence and tuned the experimental parameters to produce dual carbon-layered MC-LFP nanostructures of almost 65 ± 8 nm diameter and 350–400 nm length. The novel LFP structural design simultaneously decreased the charge transfer resistance, accelerated the Li-ion intercalation/deintercalation kinetics, and shortened the electro-ionic charge transfer path length, thus improving the battery rate performance. Consequently, discharge capacities of 168 mA h g−1 at 0.1C and 138 mA h g−1 at 10C were achieved. Moreover, the MC-LFP showed excellent charge–discharge cycling stability, with only 7% capacity fading at 10C after 1000 cycles. Thus, the dual carbon-layered biomimetic mitochondrion LFP as a cathode material possesses significant potential for the development of high-performance Li+-ion batteries.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...