Acid-durable electride with layered ruthenium for ammonia synthesis: boosting the activity via selective etching†
Abstract
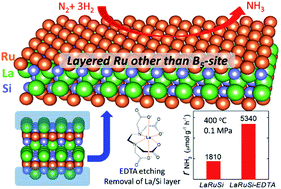
Ruthenium (Ru) loaded catalysts are of significant interest for ammonia synthesis under mild reaction conditions. The B5 sites have been reported as the active sites for ammonia formation, i.e., Ru with other coordinations were inactive, which has limited the utilization efficiency of Ru metal. The implantation of Ru into intermetallic compounds is considered to be a promising approach to tune the catalytic activity and utilization efficiency of Ru. Here we report an acid-durable electride, LnRuSi (Ln = La, Ce, Pr and Nd), as a B5-site-free Ru catalyst. The active Ru plane with a negative charge is selectively exposed by chemical etching using disodium dihydrogen ethylenediaminetetraacetate (EDTA-2Na) acid, which leads to 2–4-fold enhancement in the ammonia formation rate compared with that of the original catalyst. The turnover frequency (TOF) of LnRuSi is estimated to be approximately 0.06 s−1, which is 600 times higher than that of pure Ru powder. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations revealed that the dissociation of N2 occurs easily on the exposed Ru plane of LaRuSi. This systematic study provides firm evidence that layered Ru with a negative charge in LnRuSi is a new type of active site that differs significantly from B5 sites.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...