The nuclear export inhibitor aminoratjadone is a potent effector in extracellular-targeted drug conjugates†
Abstract
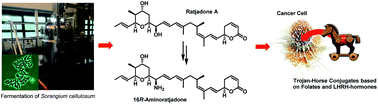
The concept of targeted drug conjugates has been successfully translated to clinical practice in oncology. Whereas the majority of cytotoxic effectors in drug conjugates are directed against either DNA or tubulin, our study aimed to validate nuclear export inhibition as a novel effector principle in drug conjugates. For this purpose, a semisynthetic route starting from the natural product ratjadone A, a potent nuclear export inhibitor, has been developed. The biological evaluation of ratjadones functionalized at the 16-position revealed that oxo- and amino-analogues had very high potencies against cancer cell lines (e.g. 16R-aminoratjadone 16 with IC50 = 260 pM against MCF-7 cells, or 19-oxoratjadone 14 with IC50 = 100 pM against A-549 cells). Mechanistically, the conjugates retained a nuclear export inhibitory activity through binding CRM1. To demonstrate a proof-of-principle for cellular targeting, folate- and luteinizing hormone releasing hormone (LHRH)-based carrier molecules were synthesized and coupled to aminoratjadones as well as fluorescein for cellular efficacy and imaging studies, respectively. The Trojan–Horse conjugates selectively addressed receptor-positive cell lines and were highly potent inhibitors of their proliferation. For example, the folate conjugate FA-7-Val-Cit-pABA-16R-aminoratjadone had an IC50 of 34.3 nM, and the LHRH conjugate D-Orn-Gose-Val-Cit-pABA-16R-aminoratjadone had an IC50 of 12.8 nM. The results demonstrate that nuclear export inhibition is a promising mode-of-action for extracellular-targeted drug conjugate payloads.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...