Addressing the properties of “Metallo-DNA” with a Ag(i)-mediated supramolecular duplex†
Abstract
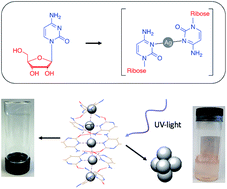
The silver-nucleoside complex [Ag(I)-(N3-cytidine)2], 1, self-assembles to form a supramolecular metal-mediated base-pair array highly analogous to those seen in metallo-DNA. A combination of complementary hydrogen-bonding, hydrophobic and argentophilic interactions drive the formation of a double-helix with a continuous silver core. Electrical measurements on 1 show that despite having Ag⋯Ag distances within <5% of the metallic radii, the material is electrically insulating. This is due to the electronic structure which features a filled valence band, an empty conduction band dominated by the ligand, and a band gap of 2.5 eV. Hence, as-prepared, such Ag(I)-DNA systems should not be considered molecular nanowires but, at best, proto-wires. The structural features seen in 1 are essentially retained in the corresponding organogel which exhibits thixotropic self-healing that can be attributed to the reversible nature of the intermolecular interactions. Photo-reduced samples of the gel exhibit luminescence confirming that these poly-cytidine sequences appropriately pre-configure silver ions for the formation of quantum-confined metal clusters in line with contemporary views on DNA-templated clusters. Microscopy data reveals the resulting metal cluster/particles are approximately spherical and crystalline with lattice spacing (111) similar to bulk Ag.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...