The fate of bromine after temperature-induced dehydrogenation of on-surface synthesized bisheptahelicene†
Abstract
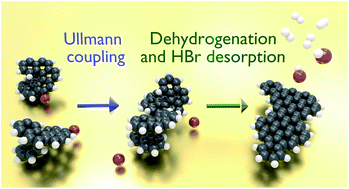
The on-surface synthesis of bisheptahelicene by Ullmann coupling of 9-bromoheptahelicene on Au(111) and its temperature-induced dehydrogenation is studied using temperature-programmed reaction spectroscopy and time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry. Specific dehydrogenation products of bisheptahelicene after loss of 6, 8 and 10 hydrogen atoms are identified, corresponding to molecules having undergone Diels–Alder transformations and intramolecular C–C coupling reactions. By combining with atomic hydrogen produced by dehydrogenation, the Ullmann coupling side-product bromine desorbs as HBr. H2 desorption emerges only after all Br has desorbed. Such characteristic behavior is explained by a kinetic model which explicitly considers the coverage of transient atomic H on the surface. Heating experiments performed with saturated layers of different Br-containing molecules reveal that the onset of HBr desorption depends strictly on the dehydrogenation step and therefore on the structure of the molecules.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...