Lysine carbonylation is a previously unrecognized contributor to peroxidase activation of cytochrome c by chloramine-T†
Abstract
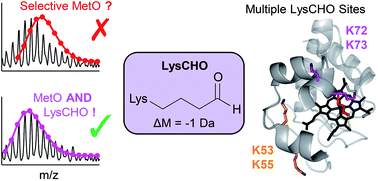
The peroxidase activity of cytochrome c (cyt c) plays a key role during apoptosis. Peroxidase catalysis requires a vacant Fe coordination site, i.e., cyt c must undergo an activation process involving structural changes that rupture the native Met80–Fe contact. A common strategy for dissociating this bond is the conversion of Met80 to sulfoxide (MetO). It is widely believed that this MetO formation in itself is sufficient for cyt c activation. This notion originates from studies on chloramine-T-treated cyt c (CT-cyt c) which represents a standard model for the peroxidase activated state. CT-cyt c is considered to be a “clean” species that has undergone selective MetO formation, without any other modifications. Using optical, chromatographic, and mass spectrometry techniques, the current work demonstrates that CT-induced activation of cyt c is more complicated than previously thought. MetO formation alone results in only marginal peroxidase activity, because dissociation of the Met80–Fe bond triggers alternative ligation scenarios where Lys residues interfere with access to the heme. We found that CT causes not only MetO formation, but also carbonylation of several Lys residues. Carbonylation is associated with −1 Da mass shifts that have gone undetected in the CT-cyt c literature. Proteoforms possessing both MetO and Lys carbonylation exhibit almost fourfold higher peroxidase activity than those with MetO alone. Carbonylation abrogates the capability of Lys to coordinate the heme, thereby freeing up the distal site as required for an active peroxidase. Previous studies on CT-cyt c may have inadvertently examined carbonylated proteoforms, potentially misattributing effects of carbonylation to solely MetO formation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...